How to enable DHCP
Management of DHCP and IP ranges is a key element of configuring and managing MAAS. This article will help you learn:
MAAS enlists and commissions machines through the use of its DHCP server running on an untagged VLAN. Although this MAAS-managed DHCP can also be part of the deploy phase, an external DHCP server can optionally be used instead for this purpose. If MAAS detects an external DHCP server, it will display it on the rack controller’s page, accessible by selecting ‘Controllers’ from the top menu in the web UI.
In addition, the machine subnet is usually on the untagged VLAN. If not, you will need to route DHCP packets between the subnet and the MAAS-provided DHCP subnet. It is also possible to forward DHCP traffic from one VLAN to another using an external DHCP relay service.
This documentation presupposes that MAAS-managed DHCP is used to enlist and commission machines. Using an external DHCP server for enlistment and commissioning may work, but note that this is not supported. MAAS cannot manage an external DHCP server, nor can it keep leases synchronised when you return a machine to the pool.
This article will help you learn:
- How to enable MAAS-managed DHCP
- How to resolve IP conflicts
- How to extend a reserved dynamic IP range
- How to configure external DHCP
- How to use a DHCP relay
- How to customise MAAS with DHCP snippets
How to enable MAAS-managed DHCP
MAAS-managed DHCP needs a reserved dynamic IP range to enlist and commission machines. You should create such a range when you are enabling DHCP with the web UI.
To enable MAAS-managed DHCP, under the ‘Subnets’ page select the desired VLAN and then:
- Under the ‘Take action’ button select ‘Provide DHCP’. A new window will appear.
- Select the primary rack controller. For DHCP HA, select both the primary and the secondary.
- Create a reserved, dynamic IP range. Fill in the fields ‘Dynamic range start IP’ and ‘Dynamic range end IP’.
- Apply your changes with the ‘Provide DHCP’ button.
Now, addresses in this range will get assigned to machines that are being either enlisted or commissioned. In addition, if you are deploying a machine that has an interface connected to the untagged VLAN, and it has an IP assignment mode set to ‘DHCP,’ then it will also get an address in this range.
In some cases, MAAS manages a subnet that is not empty, which could result in MAAS assigning a duplicate IP address. MAAS is capable of detecting IPs in use on a subnet. Be aware that there are two caveats:
-
If a previously-assigned NIC is in a quiescent state or turned off, MAAS may not detect it before duplicating an IP address.
-
At least one rack controller must have access to the IP-assigned machine in order for this feature to work.
MAAS also recognises when the subnet ARP cache is full, so that it can re-check the oldest IPs added to the cache to search for free IP addresses.
How to extend a reserved dynamic IP range
If necessary, it is possible to add further portions of the subnet to the dynamic IP range (see below). Furthermore, since you enabled DHCP on a VLAN basis and a VLAN can contain multiple subnets, it is possible to add a portion from those subnets as well. Just select the subnet under the ‘Subnets’ page and reserve a dynamic range. DHCP will be enabled automatically.
How to configure external DHCP
If an external DHCP server is used to deploy machines, then a reserved IP range should be created to prevent the address namespace from being corrupted. For instance, address conflicts may occur if you set a machine’s IP assignment mode to ‘Auto assign’ in the context of an external DHCP server. See below to create such a range. It should correspond to the lease range of the external server.
You should not enable DHCP relays in MAAS without sufficient planning. In particular, MAAS does not provide the actual relay. It must be set up as an external service by the administrator. What MAAS does provide is the DHCP configuration that MAAS-managed DHCP requires in order to satisfy any client requests relayed from another VLAN.
To relay from one VLAN (source) to another VLAN (target):
-
Ensure the target VLAN has DHCP enabled.
-
Set up the external relay. This relay is set up independently from MAAS. See DHCP relay for software suggestions.
-
Configure MAAS-managed DHCP. Navigate to the source VLAN page and select the ‘Relay DHCP’ action. Fill in the fields in the resulting form. The crucial setting is the target VLAN (‘Relay VLAN’). Press the ‘Relay DHCP’ button to finish.
How to customise MAAS with DHCP snippets
When MAAS manages DHCP, you customise it through the use of DHCP snippets. These are user-defined configuration options that can be applied either globally, per subnet, or per machine. You apply a global snippet to all VLANs, subnets, and machines. All three types end up in /var/snap/maas/common/maas/dhcpd.conf or /var/snap/maas/common/maas/dhcpd6.conf. Be aware that if you edit these files directly, you will need to sudo to root, as there is no maas user in the snap (all relevant files are owned by root). For information on what options to use, refer to the dhcpd.conf man page↗.
NOTE:
Modifications made directly to dhcpd.conf.template or dhcpd6.conf.template are not supported.
To manage snippets, as an admin, open the ‘Settings’ page and click on the ‘DHCP snippets’ tab.
For example, to create a new snippet press ‘Add custom snippet’. In the resulting window, choose a name and type for it and enter its associated DHCP configuration. Click ‘Save snippet’ to apply the change, and make sure to activate the checkbox in the ‘Enabled’ column of the snippets list.
In MAAS-managed networks, you can further manage your subnets with a reserved range of IP addresses. You can reserve IP addresses by adding one or more reserved ranges to a subnet configuration. You can define two types of ranges: reserved ranges and reserved dynamic ranges.
A reserved range operates differently depending on whether the subnet is managed or unmanaged. For a managed (subnet), MAAS will never assign IP addresses inside this range. You can use this range for anything, such as infrastructure systems, network hardware, external DHCP, or an OpenStack namespace. For an unmanaged (subnet), MAAS will only assign IP addresses inside this range – but MAAS can assign any IP within this range.
A reserved dynamic range is used by MAAS for enlisting, commissioning and, if enabled, MAAS-managed DHCP on the machine’s VLAN during commissioning and deployment. If created with the Web UI, an initial range is created as part of the DHCP enablement process. MAAS never uses IP addresses from this range for an unmanaged subnet.
This section gives specific instructions about creating and managing IP ranges; it will help you learn:
To create a range with the web UI, choose the “Subnets” option across the top:
In the “SUBNET” column, choose the subnet for which you want to create an IP range(s):
Scroll down to “Reserved ranges” on the subnet screen and click on the “Reserve range” drop-down:
Choose ‘Reserve range’ or ‘Reserve dynamic range’. If you choose the latter, MAAS will automatically provide DHCP for enlistment and commissioning provided that the associated VLAN has DHCP enabled.
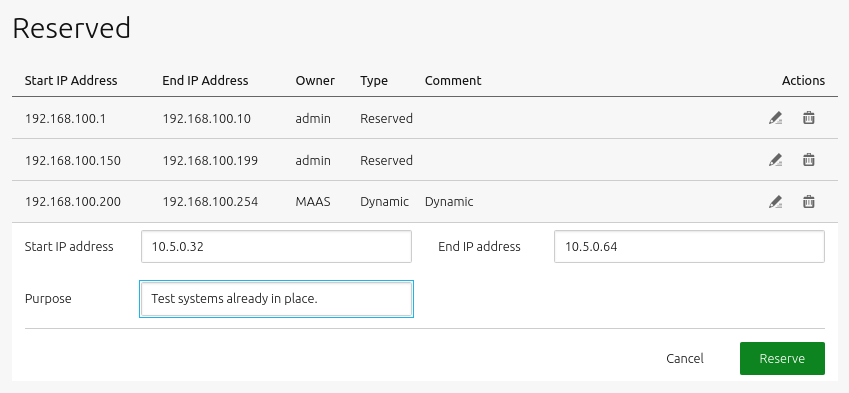
When you choose either of those two options, a window will appear allowing you to enter start and end addresses for the range as well as a comment.
Below is an example window when creating a ‘reserved range’ (the windows are identical):
Click the ‘Reserve’ button when done.
How to edit an existing IP range
Click the ‘Menu’ button at the far right of the row corresponding to the subnet in question and select ‘Edit reserved range’ from the menu that appears. Edit the fields as desired and click the ‘Save’ button.
How to delete an existing IP range
Select ‘Remove range’ from the menu that appears when clicking the ‘Menu’ button at the far right of the row corresponding to the subnet in question.